IT Infrastructure and Basic Services
New Data Center
ITSC has been collaborating with the Facilities Management Office on the development of a new data center for the University. It is now near completion.
The new data center is located on 2/F near Lift 19, just next to the existing data center that was put into use since the University campus was built more than 25 years ago. To cope with new requirements in computing and sustainable smart campus, compact and energy-efficient hot-aisle containment facilities are deployed to provide 70 equipment rack space. It is intended not only for meeting the increasing demand in research IT and high performance computing (HPC), but also for the optimization of space and energy efficiencies in data center operations through consolidation as well as adoption of software-defined technologies and green IT.

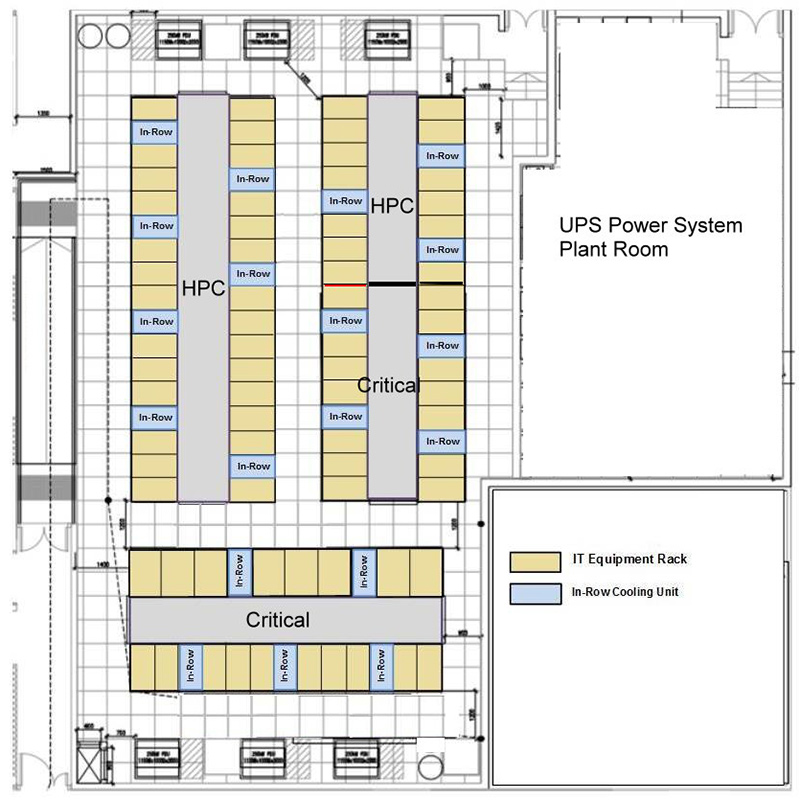
The new data center will start to operate in early November 2018 when migration from existing data center will commence. It is expected to be fully operational in June 2019 following the completion of the new power transformers upgrade work.
Meanwhile, the new data center represents an important milestone in the journey to modernize the University IT infrastructure towards a software-defined cloud-based architecture. The new data center will serve as the primary powerhouse driving the campus network and various mission-critical IT infrastructure and systems on-premises; and will seamlessly tap into the public cloud infrastructure when those become available and affordable.
Internet of Things (IoT) Network at HKUST Campus
To support a sustainable smart campus, we need to extend the campus network to cover smart sensors, controls and devices to be installed across the University campus by different interest groups of the University community. To this end, we have started to implement an Internet of Things (IoT) network infrastructure based on the LoRaWAN (Low-power, Long-range Wide Area Network) technology and integrate it with the existing campus network based on TCP/IP.
The LoRaWAN IoT Network provides a centralized, standard-based open infrastructure for collecting the data from low-powered smart sensors installed across the campus, and also controlling these smart devices in certain use cases. Various types of sensors can be deployed depending on the application areas, and the sensor data collected will be stored in a centralized open data platform, accessible by authorized teams for different usages such as Fault Monitoring, Energy Management, Real Time Ecosystem Monitoring, Classroom Access Control, etc.
Here are some practical examples of using IoT technologies:
- Monitor CO2 levels in lecture theatres and study areas, and automatically adjust ventilation to prevent drowsiness and create a more comfortable atmosphere
- Smart Toilet System consists of People Density Counter and Ammonia Sensors, and remotely monitors cleaning status and usage of restrooms. Cleaners can be dispatched as needed instead of fixed intervals
- Facilities managers can monitor energy usage and efficiency of buildings leading to greener solutions.
A pilot LoRaWAN IoT Network with 5 gateways is being set up and will be ready soon. At present, ITSC is working with Facilities Management Office on some prototype application scenarios. If the results are promising, we will seek for funding to further extend the LoRaWAN network to a full campus coverage.
In case you are interested in participating in or knowing more about this LoRaWAN project, please feel free to contact Mr. C.S. Wong at ccsing@ust.hk.

Open Data Platform for Internet of Things (IoT)
Bill Fung, IT Security Specialist
In addition to the IoT network infrastructure mentioned above, ITSC is also working on an Open Data Platform for IoT data collection and retrieval. The Open Data Platform is based on Elastic Stack which is a group of open source products designed to help users take data from any type of sources and in any format; and search, analyze, as well as visualize that data in real time. There are 3 major components of the Elastic Stack (commonly called ELK Stack):

Elasticsearch -- a distributed search and analytics engine (which is RESTful and built on top of Apache Lucene, and data could be accessed in JSON format). The RESTful interface implements the so-called CRUD data manipulation operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) through HTTP POST, GET, PUT, DELETE operations. Users are allowed to access their authorized data through RESTful API, which is supported in different programming languages.
Logstash -- a server side data processing pipeline that ingests data from a multitude of sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends to Elasticsearch. It supports many different types of inputs, including common ones like syslog, websocket, file based, beats, etc.
Kibana -- a data visualization and exploration tool for Elasticsearch, and can facilitate easy data presentation in a dashboard manner
ITSC treats data seriously and data security is always our prime focus. The Elastic Stack supports authorization by users and roles. It also supports multitenancy and granular access control. In order to prevent snooping, tampering and sniffing, the data is encrypted with SSL/TLS in the network transmission. The flexible design architecture of Elastic Stack will enable us to develop a flexible and highly scalable data platform.
At present, ITSC has set up a small pilot implementation of the Open Data Platform for experimental IoT projects. We are seeking funding for an enterprise scale implementation, including the support of unsupervised machine learning capability. If you have any projects in mind that you think may ride on this data platform or if you want more details, please feel free to contact us.
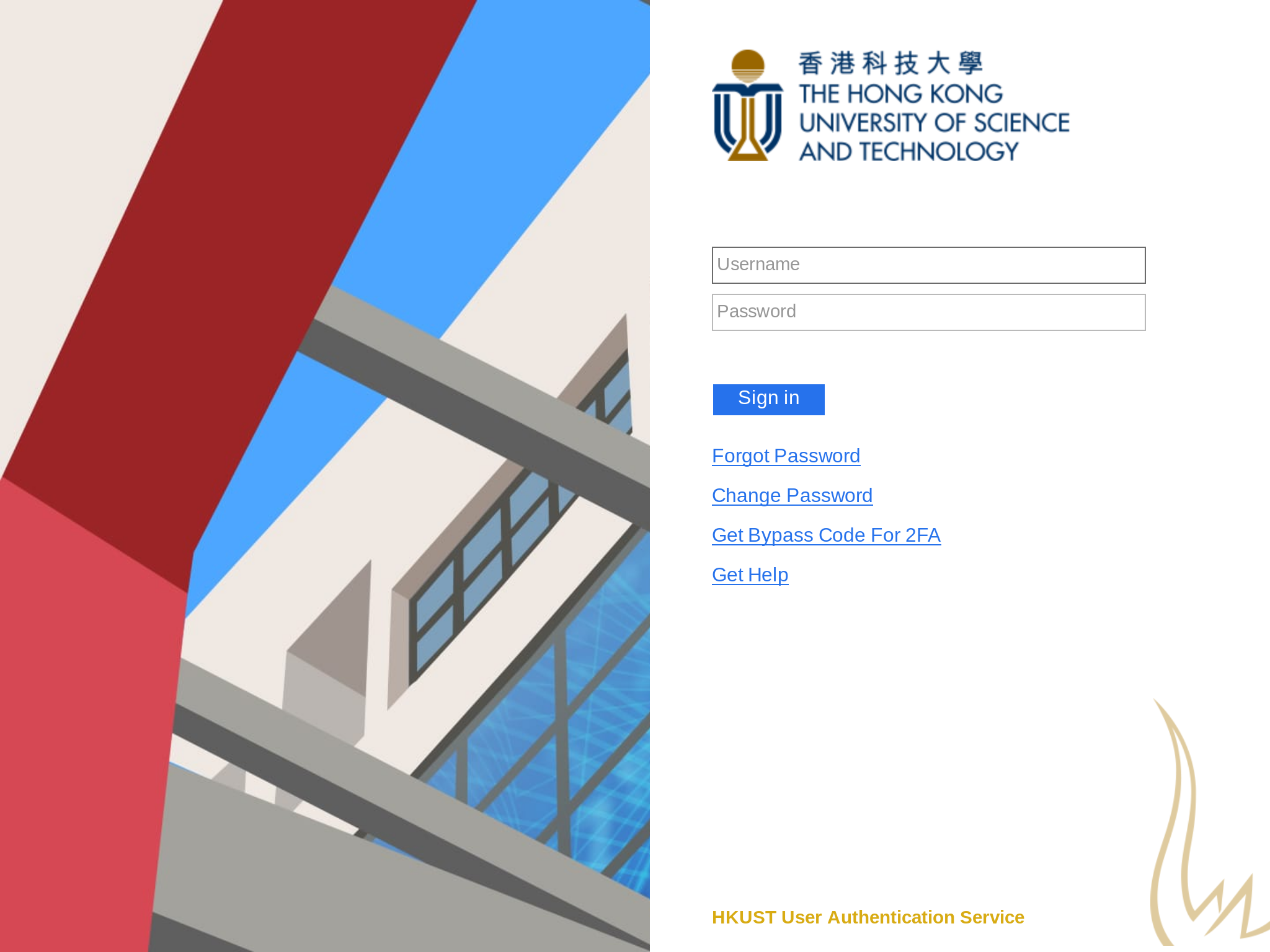
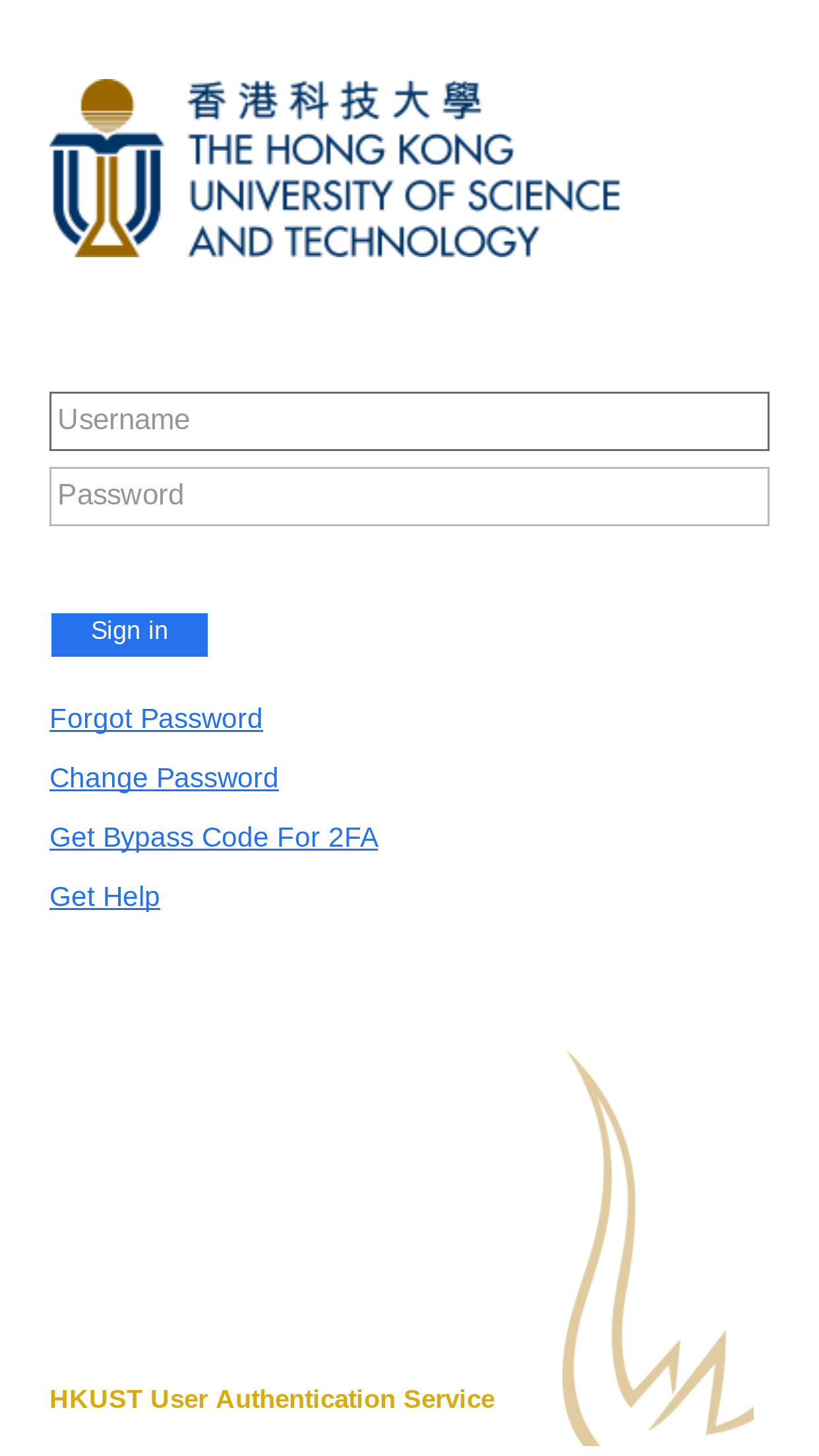
New User Interface for User Authentication
How a user authenticates himself or herself to online services constitutes an important part of user experience. The open-source Central Authentication System (CAS) has been the standard means for user authentication at HKUST, supplemented by Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) for access to Office 365 services. The user interfaces of CAS and ADFS, however, are quite different due to intrinsic differences in underlying technologies.
With the help from the Publishing Technology Center, we have re-designed the user interfaces of CAS and ADFS in the hope to make them more user friendly and look more consistent. The new interfaces will be used to access online services of HKUST starting from later this month. They will also lay the foundation for support of more advanced features pertaining to user authentication, such as access federation and mobile apps. Stay tuned.
Do you know the publication of University Communications Directory is available online?
The University Communications Directory is published as a handy booklet biannually. Since June 2018, the latest version of the copy is also accessible online, through the Staff Intranet. Staff members may consider using this online version and think again before placing an order for the booklet next time. The number of ordered copies for the recent September issue has been reduced by 25% compared with last year. Let’s join hands and continue this effort, in support of a sustainable environment.